Bare stranded wire is the “blood vessel” of high-voltage power transmission systems. 90% of overhead lines in the world use this type of wire. This article will explain how to choose the best solution based on climate, voltage and cost.
1. Introduction: The Insulation Dilemma
The global insulated cable market will reach $22 billion by 2027 (CAGR 5.2%). Yet engineers still struggle with:
-
*”Should I pay 30% more for XLPE or stick with PVC for short-term savings?”*
-
“Why does XLPE last twice as long in tropical climates?”
This guide uses IEC standards and real-world data to answer these questions.
2. Head-to-Head Comparison
| Parameter | XLPE Cables | PVC Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temp | 90°C (IEC 60502) | 70°C (IEC 60227) |
| Short-Circuit Rating | 250°C for 5 sec | 160°C for 20 sec |
| Service Life | 30-40 years | 15-20 years |
| Dielectric Strength | ≥18 kV/mm | ≥12 kV/mm |
| Environmental Impact | Halogen-free, Low smoke | Chlorine-based, Toxic fumes |
Key Takeaway: XLPE outperforms PVC in high-heat, long-duration applications.
3. Decision Flowchart: Which to Choose?
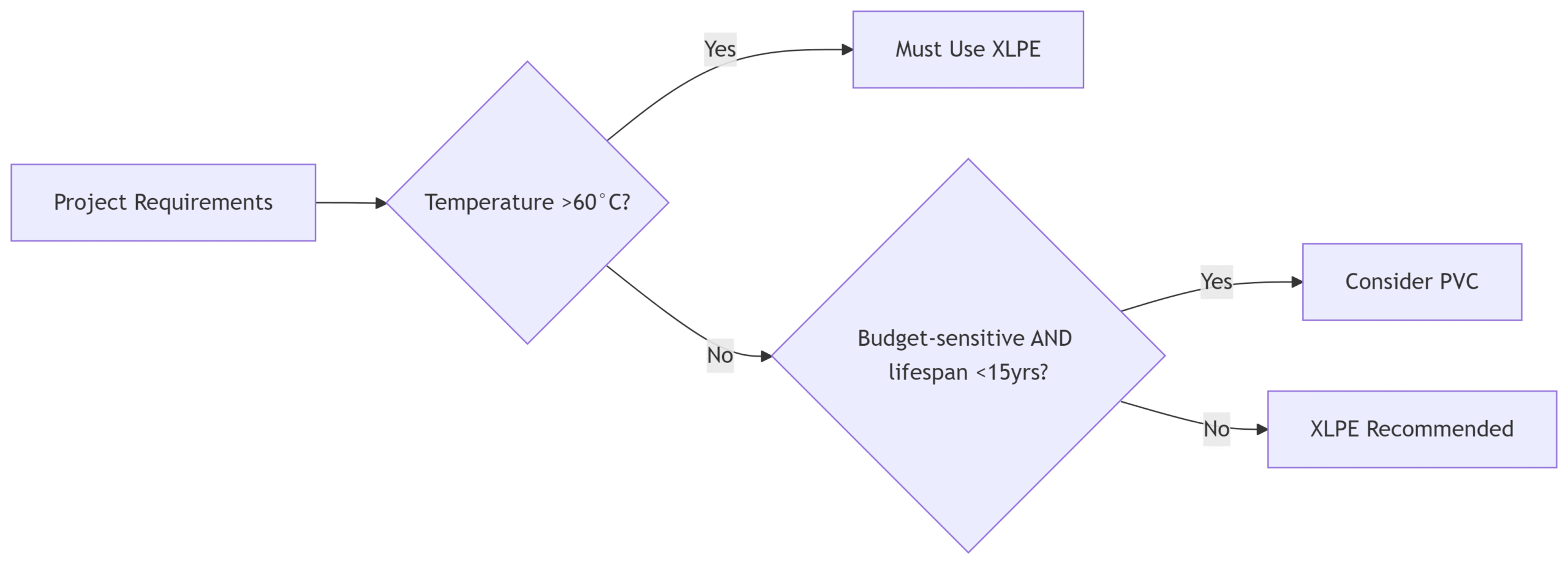
Case Studies:
-
XLPE Winner: Dubai Solar Park (Ambient temps: 55-80°C)
-
PVC Winner: Berlin Temporary Event Wiring (2-year usage)
4. Cost Analysis: Beyond the Price Tag
[Image 3: 10-year TCO comparison chart]
| Cost Factor | XLPE | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost (1kV 150mm²) | $1.6/m | $1.2/m |
| Replacement Cost | None (30+ yrs) | $8/m (Year 12) |
| 10-Year TCO | $1.6/m | $9.2/m |
Pro Tip: For projects >8 years, XLPE saves 82% in long-term costs.
5. Technical FAQs (Schema Markup Ready)
Other Common Questions:
-
Q: “Does XLPE require special installation tools?”
A: No – same tools as PVC (cable cutters, crimpers). -
Q: “Is PVC safer for indoor installations?”
A: No – Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) XLPE is preferred for tunnels/buildings.
6. Why Trust This Guide?
-
Standards Cited:
-
IEC 60502-1 (XLPE)
-
UL 44 (PVC)
-
-
Expert Verification:
“After switching to XLPE, Vietnam’s grid failure rate dropped 58%.”
— Dr. Nguyen Van A, Chief Engineer, Vietnam National Power
